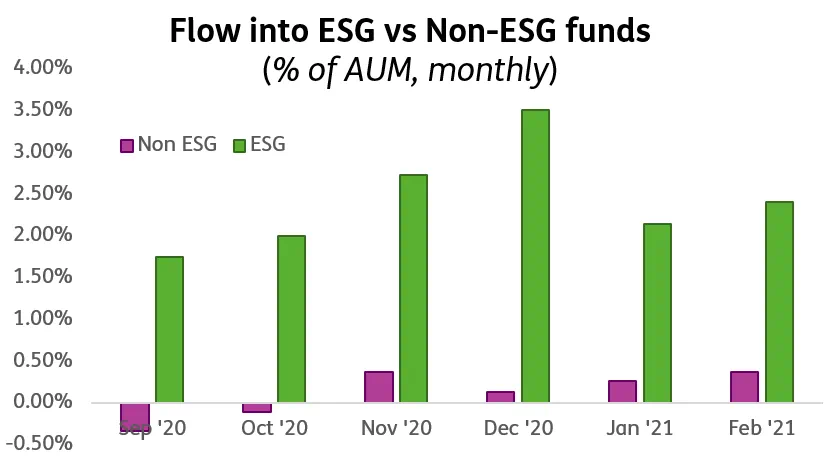
The massive flows of money into environmental, social and governance (ESG) investments over 2020 continued into January and February, according to EPFR data. But, without better ESG reporting standards, this wave of money will fall short of the desired impact.
Sustainable investing has long been hampered by patchy or confusing measurement and reporting, leaving the door open for some asset managers to make overly positive claims about the impact of their activities.
As sustainable investing becomes more mainstream, investors will demand better, more standardized and comparable information. Asset managers, and those that guide and regulate them, will have to respond.
But one major obstacle is the bewildering plethora of ESG standards and metrics that already exist. Turning these into a simple, cohesive set of standards could be like turning round a huge old tanker in a hurricane.
Setters respond
Global standard setters are finally moving to solve the problem by working together on aligning or integrating their benchmarks.
Last year, the World Economic Forum (WEF) teamed up with the Big Four accounting firms to develop new international metrics for sustainable value creation, which aim to help companies and investors align reporting on ESG factors. Since launch, over 60 companies – including Bank of America, MasterCard and Dell – have committed to using the metrics.
The International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) Foundation is consulting on a new Sustainability Standards Board.
And five bodies that together guide most of world’s sustainability reporting – The Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), CDP (previously Carbon Disclosure Project), Sustainability Accounting Standards Board, Climate Disclosure Standards Board, and International Integrated Reporting Council – have stated their intent to work together on their frameworks.
Growing momentum
These initiatives will kickstart global cohesion in ESG standards. But success will depend on how tough the eventual agreed standards are and how practical they are for companies and investors to use.
One critical question is how much the integrated initiatives will align with the European Union’s already tough regulatory stance. The EU is recognized as leading on ESG reporting with its robust Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulations (SFDR), the first level of which came into force on 10 March 2021.
Early indicators are that many of the global initiatives will aim to align with SFDR where possible. But this will create extreme challenges for many asset managers around the world. Those with operations in EU countries are managing to comply with the simpler SFDR level one regulations. However, the level two rules, due to enforce in June 2023, are more much onerous, especially around measuring and reporting adverse impacts.
This strict approach is necessary to make standards effective in tackling issues such as climate change. But it will take significant resources for asset managers to comply and is likely to benefit larger firms with greater research budgets.
One problem is that much of the necessary data does not exist yet or is not easily accessible from companies in a clearly defined and searchable format. This could make meeting some level two SFDR requirements difficult, or even impossible.
To comply and drive genuine change, firms will need data that assesses impacts throughout their supply chain and beyond. Global harmonizing initiatives, alongside SFDR, will be a first step on the long journey towards collecting, measuring and analyzing this information efficiently and effectively.
Until we have systematic provision of such ESG data, the effects will be limited. But momentum is building and huge changes are on the horizon.
Did you find this useful? Get our EPFR Insights delivered to your inbox.